
ELAMIPRETIDE (SS-31)

SS-31, also known as Bendavia or elamipretide, is a mitochondria-targeting peptide that accumulates in mitochondria and scavenges reactive oxygen species. It's a small, cell-permeable molecule that selectively targets the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it interacts with cardiolipin, a key phospholipid component. This interaction helps stabilize mitochondrial membranes, optimize electron transport chain function, and mitigate oxidative stress.
SS-31 Peptide Benefits
- Mitochondrial Protection: SS-31 enhances the structural integrity and function of mitochondria, protecting them from damage caused by oxidative stress, a major contributor to various diseases and aging processes.
- Energy Production: By preserving mitochondrial function, SS-31 promotes efficient ATP production through the electron transport chain, supporting cellular energy metabolism.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: SS-31 has been shown to reduce inflammation by inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and dampening the activation of inflammatory pathways within cells.
- Cardioprotection: Studies have demonstrated the cardioprotective effects of SS-31, including its ability to improve cardiac function, reduce ischemia/reperfusion injury, and enhance recovery after heart attacks.
- Neuroprotection: SS-31 shows promise in protecting neurons from oxidative damage and improving mitochondrial function in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Possible Uses For SS-31
- Treatment of Mitochondrial Disorders: SS-31 holds potential as a therapeutic agent for various mitochondrial disorders, including mitochondrial myopathies, Leigh syndrome, and mitochondrial encephalopathy, among others.
- Heart Disease: Given its cardioprotective effects, SS-31 could be used to prevent or treat heart failure, myocardial infarction, and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Neurological Disorders: SS-31 may have applications in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
- Anti-aging Interventions: As mitochondrial dysfunction is a hallmark of aging, SS-31 could potentially be used as an anti-aging intervention to maintain mitochondrial health and delay age-related decline.
- Athletic Performance Enhancement: By improving cellular energy production and reducing oxidative stress, SS-31 may have applications in enhancing athletic performance and aiding in recovery from strenuous exercise.
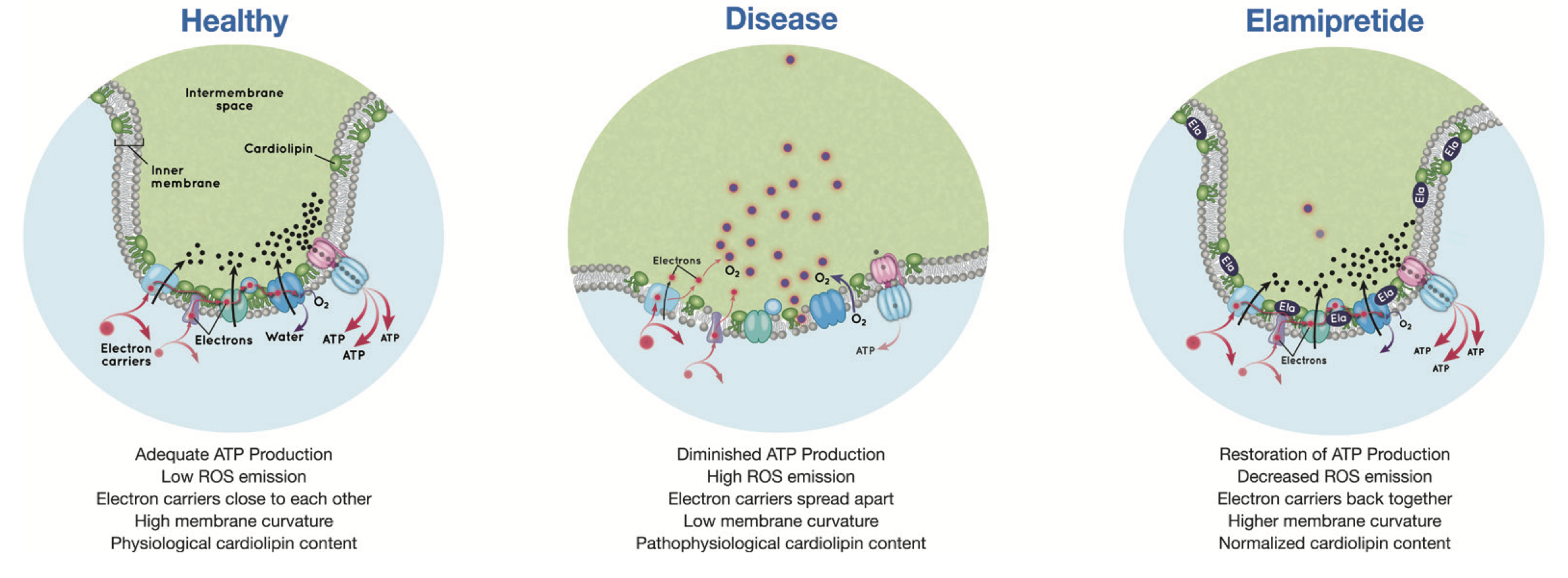
Uses and Indications for SS-31 in age related disease:
- Mitochondrial Health: SS-31 has shown promise in preserving mitochondrial function, which is crucial for cellular energy production and overall vitality. As individuals age, mitochondrial dysfunction becomes increasingly prevalent, contributing to age-related decline in various tissues and organs. SS-31's ability to protect mitochondria from oxidative damage and improve their function makes it a promising candidate for combating age-related mitochondrial dysfunction.
- Reducing Oxidative Stress: Oxidative stress is a hallmark of aging and is implicated in the development of numerous age-related diseases, including cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic syndrome. SS-31's antioxidant properties enable it to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative damage, thereby potentially mitigating age-related oxidative stress and its associated pathologies.
- Cardioprotection: Aging is often accompanied by an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart failure, atherosclerosis, and myocardial infarction. SS-31 has demonstrated cardioprotective effects in preclinical studies, including the preservation of cardiac function, reduction of ischemia/reperfusion injury, and improvement of vascular health. These properties suggest that SS-31 could be beneficial in promoting cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of age-related cardiovascular complications.
- Neuroprotection: Age-related neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, are characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and neuronal damage. SS-31 has shown neuroprotective effects in preclinical models by preserving mitochondrial function, reducing oxidative stress, and promoting neuronal survival. This suggests that SS-31 may have potential applications in preventing or slowing the progression of age-related neurodegenerative disorders.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of aging and is associated with the development of age-related diseases, including arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. SS-31 has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties, including the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine production and the suppression of inflammatory signaling pathways. By attenuating age-related inflammation, SS-31 may help reduce the risk of inflammatory diseases and promote healthy aging.
Overall, SS-31 holds significant promise as a therapeutic agent for promoting healthy aging and combating age-related decline. Its ability to preserve mitochondrial function, reduce oxidative stress, protect against cardiovascular and neurological diseases, and mitigate inflammation makes it a valuable candidate for anti-aging interventions. Further research and clinical trials are needed to fully elucidate the potential benefits and therapeutic applications of SS-31 in promoting healthy aging and extending healthspan.
Safety
SS-31 treatment is administered via subcutaneous injection. It leads to a few adverse events, though mostly mild. The most common adverse event with SS-31 is injection site reaction.
Research
Karaa A. Bertini E. Carelli V. Cohen B.H. Enns G.M. Falk M.J. Goldstein A. Gorman G.S. Haas R. Hirano M. et al. Efficacy and safety of elamipretide in individuals with primary mitochondrial myopathy: the MMPOWER-3 randomized clinical trial. Neurology. 2023; 101: e238-e252
Karaa A, Haas R, Goldstein A, Vockley J, Weaver WD, Cohen BH. Randomized dose-escalation trial of elamipretide in adults with primary mitochondrial myopathy. Neurology. 2018;90(14):e1212-e1221
Birk A, Liu S, Soong Y, et al. The mitochondrial-targeted compound SS-31 reenergizes ischemic mitochondria by interacting with cardiolipin. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;24(8):1250-1261.
Brown DA, Hale SL, Baines CP, et al. Reduction of early reperfusion injury with the mitochondria-targeting peptide Bendavia. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014;19(1):121-132
Roshanravan B, Liu SZ, Ali AS, et al. In vivo mitochondrial ATP production is improved in older adult skeletal muscle after a single dose of elamipretide in a randomized trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(7):e0253849.
Stauffer B, Sparagna G, Chau S, et al. MTP131, a cardiolipin targeting peptide, improves mitochondrial activity in the failing human heart. Eur J Heart Fail Abstr Suppl. 2016;18:289.
Liu Y, Fu H, Wu Y, Nie B, Liu F, Wang T, Xiao W, Yang S, Kan M, Fan L. Elamipretide (SS-31) Improves Functional Connectivity in Hippocampus and Other Related Regions Following Prolonged Neuroinflammation Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in Aged Rats. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Mar 1;13:600484. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.600484. PMID: 33732135; PMCID: PMC7956963.
Nhu NT, Xiao SY, Liu Y, et al. Neuroprotective Effects of a Small Mitochondrially-Targeted Tetrapeptide Elamipretide in Neurodegeneration. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience. 2021 ;15:747901. DOI: 10.3389/fnint.2021.747901. PMID: 35111001; PMCID: PMC8801496.
Lindsay A. Seewald, Isabella G. Sabino, Kaylee L. Montney, Michelle L. Delco. Synovial Fluid Mitochondrial DNA Concentration Reflects the Degree of Cartilage Damage After Naturally Occurring Articular Injury. bioRxiv 2021.08.26.457571; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.26.457571
Zhu Y, Luo M, Bai X, Li J, Nie P, Li B, Luo P. SS-31, a Mitochondria-Targeting Peptide, Ameliorates Kidney Disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jun 6;2022:1295509. doi: 10.1155/2022/1295509. PMID: 35707274; PMCID: PMC9192202.
Cano Sanchez M, Lancel S, Boulanger E, Neviere R. Targeting Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Treatment of Impaired Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants. 2018; 7(8):98.
Jeremy A. Whitson, Miguel Martín-Pérez, Tong Zhang, Matthew J. Gaffrey, Gennifer E.Merrihew, Eric Huang, Collin C. White, Terrance J. Kavanagh, Wei-Jun Qian, Matthew D.Campbell, Michael J. MacCoss, David J. Marcinek, Judit Villén, Peter S. Rabinovitch.Elamipretide (SS-31) Treatment Attenuates Age-Associated Post-Translational Modifications of Heart Proteins. bioRxiv 2021.08.06.455402; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.06.455402
Smuder A. J., Roberts B. M., Wiggs M. P., Kwon O. Sung, Yoo J., Christou D. D., Fuller D. D., Szeto H. H., Judge A. R. Pharmacological targeting of mitochondrial function and reactive oxygen species production prevents colon 26 cancer-induced cardiorespiratory muscle weakness. Oncotarget. 2020; 11: 3502-3514.
Calvo-Rodriguez, M., Kharitonova, E.K., Snyder, A.C. et al. Real-time imaging of mitochondrial redox reveals increased mitochondrial oxidative stress associated with amyloid β aggregates in vivo in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegeneration 19, 6 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-024-00702-2