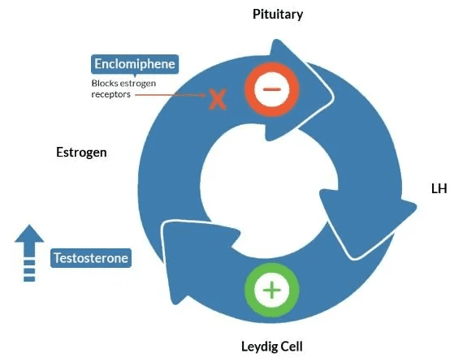
Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) and enclomiphene citrate are both common treatments for low or sub-optimal levels of testosterone. boosting properties. According to the American Urological Association, hCG is appropriate for men with testosterone deficiency who also desire to maintain fertility. HCG is an injectable medication.
Enclomiphene citrate is a newer alternative to HCG. It works by increasing testosterone while blocking the feedback effects of estrogen on the brain and testicles. Enclomiphene is an oral medication.
- Enclomiphene and HCG are both alternatives to testosterone replacement (TRT); they can help increase testosterone levels without compromising fertility.
- HCG has be associated with influencing estrogen production whereas enclomiphene blocks estrogen and does not have these effects.
- It is possible to combine enclomiphene and HCG. This combination is often used when trying to improve your sperm count after being on testosterone replacement.
ENCLOMIPHENE
Enclomiphene citrate is the purified isomer of the medication Clomid® (clomiphene citrate). It belongs to a class of drugs known as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs). These drugs bind to hypothalamic estrogen receptors in the brain, which tricks the body into thinking that it’s not getting enough estrogen. This stimulates the production of the hormones luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) to boost testosterone production.
Enclomiphene does not shut down natural testosterone production. It stimulates your body’s ability to make its own testosterone. Enclomiphene also does not increase estrogen levels.
Studies have been done comparing transdermal testosterone to enclomiphene. Researchers found that enclomiphene consistently raised total testosterone levels into the normal range while simultaneously increasing LH and FSH levels. Transdermal testosterone raised total testosterone levels but serum levels of LH and FSH decreased.
There are other studies that compared enclomiphene citrate to topical testosterone which had similar results. Both testosterone treatments increased testosterone, but those whi used topical testosterone also experienced a decline in sperm concentration.
Enclomiphene citrate side effects
Enclomiphene has an impressive safety profile and is well-tolerated without serious drug to drug interactions. The most common side effects reported include:
- High libido
- Aggression
- Acne
The following side effects are rare and have been observed in less than 4% of users:
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Hot flush
- Joint pain
- Diarrhea
HCG
HCG is produced by the placenta during pregnancy and appears in a pregnant woman’s blood and urine as early as 10 days after conception. Pregnancy tests can measure HCG levels to determine if a woman is pregnant.
Men do not produce HCG naturally. When it is introduced into the body, it will function like luteinizing hormone (LH), a hormone that the male body already produces. LH hormone targets Leydig cells in the testicles which will stimulate them to produce and release testosterone.
HCG stimulates testosterone production without affecting spermatogenesis. It has also been shown to improve semen levels in patients who were using transdermal or injectable testosterone. This is the main reason the American Urological Association has recommended HCG therapy for men with testosterone deficiency who wish to maintain their fertility. It can be used in combinaiton with selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and aromatase inhibitors (AIs).
HCG increases Testosterone
Studies have shown HCG to be an effective therapy for low testosterone. In a 2019 study, HCG was prescribed to men struggling with symptoms and complaints of low testosterone. These include low libido, lack of energy, and erectile dysfunction. Over the duration of 6 months mean testosterone improved by 49.9% from a baseline of 362 ng/dL to 519.8 ng/dL and 50% of patients reported symptom improvement with no reported side effects or complications.
Many men have also been prescribed HCG to complement their TRT therapy. It can reduce the side effects of exogenous testosterone and prevent testicular atrophy. Some men also use HCG to help maintain their testosterone levels when “cycling off” or taking a break from TRT.
HCG side effects
Side effects of HCG may include:
- Mood swings
- Headache
- Acne
- Fatigue
- Upset stomach
- Nausea
- Pain and irritation at injections site
- Weight gain
- Breast enlargement
HCG vs ENCLOMIPHENE
Studies comparing HCG vs Clomid (enclomiphene) have found that both treatments are equally effective in restoring testosterone levels without compromising fertility. Here are some differences to consider:
- Delivery Method: Enclomiphene is available in oral form while HCG is an injectable medication. HCG requires refrigeration and mixing.
- Accessibility: Due to new FDA classification, HCG was reclassified as a biologic medication and compounding HCG has been restricted. This can lower its accessibility and potentially raise costs for testosterone restoration. The brand name Pregnyl however is easily accessible. There have been talks of enclomiphene restriction but so far this has not happened. Although Enclomiphene is not FDA approved it is still available through compounding pharmacies.
Using HCG and Enclomiphene together
It may unnecessary but is possible to combine HCG therapy with enclomiphene. There is a study that looked at three groups of men. Men taking enclomiphene citrate, men taking HCG, and men taking a combination of the two. The study found that all three treatments were equally effective.
When trying to recover sperm concentration after being on TRT, it may be beneficial to combining HCG and enclomiphene. Research shows that men on TRT with azoospermia (no sperm) or severe oligozoospermia (low sperm count) have significantly improved their sperm count within an average of 4-5 months after stopping TRT when treated with HCG and enclomiphene citrate.
Improve Testosterone Levels Naturally
Normal levels of testosterone should fall between 300 and 1100. But what if your level comes back at 350, 400, or 450? It’s quite common to have your levels be close to the bottom of the normal range while experiencing some of the symptoms of low testosterone.
What should you do in that case? We recommend having a conversation a physician knowledgeable in this are to see if HCG or enclomiphene citrate are good options for you. These options can help address your symptoms and improve your testosterone levels naturally.
Research
Habous M, Giona S, Tealab A, Aziz M, Williamson B, Nassar M, Abdelrahman Z, Remeah A, Abdelkader M, Binsaleh S, Muir G. Clomiphene citrate and human chorionic gonadotropin are both effective in restoring testosterone in hypogonadism: a short-course randomized study. BJU Int. 2018 Nov;122(5):889-897. doi: 10.1111/bju.14401. Epub 2018 Jun 14. PMID: 29772111.
Wenker EP, Dupree JM, Langille GM, Kovac J, Ramasamy R, Lamb D, Mills JN, Lipshultz LI. The Use of HCG-Based Combination Therapy for Recovery of Spermatogenesis after Testosterone Use. J Sex Med. 2015 Jun;12(6):1334-7. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12890. Epub 2015 Apr 22. PMID: 25904023.
Wexler T. Enclomiphene citrate improves hormone levels while preserving sperm production in men with secondary hypogonadism. Fert Steril. Mar 2014. 102(3): 720-727
Wiehle R, Cunningham GR, Pitteloud N, Wike J, Hsu K, Fontenot GK, Rosner M, Dwyer A, Podolski J. Testosterone Restoration by Enclomiphene Citrate in Men with Secondary Hypogonadism: Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics. BJU Int. 2013 Jul 12;112(8):1188–200. doi: 10.1111/bju.12363. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 23875626; PMCID: PMC4155868.
Madhusoodanan V, Patel P, Lima TFN, Gondokusumo J, Lo E, Thirumavalavan N, Lipshultz LI, Ramasamy R. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin monotherapy for the treatment of hypogonadal symptoms in men with total testosterone > 300 ng/dL. Int Braz J Urol. 2019 Sep-Oct;45(5):1008-1012. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2019.0132. PMID: 31408289; PMCID: PMC6844348.