
THYMULIN

Thymulin: Unlocking the Secrets of Anti-Aging and Immune Regulation
The thymus gland is located in the chest behind the breastbone. Its main function is producing and training white blood cells known as T cells, which aid in immunity. White blood cells (lymphocytes) travel from your bone marrow to your thymus. The lymphocytes mature and become specialized T-cells in your thymus. These are the white blood cells responsible for fighting infections.
After the T-cells have matured, they enter your bloodstream. They travel to your lymph nodes and other organs in your lymphatic system, where they help your immune system fight disease and infection.
Your thymus gland is also part of your endocrine system. Your endocrine system makes and releases hormones that control the functions of your body. The thymus produces an array of hormones. Some of these include thymopoietin which helps production of T-cells and thymulin and thymosin which help make specialized types of T-cells to regulate immune cells. The thymus also synthesizes hormones such as insulin and melatonin.
The thymus is relatively large in infants and children. After puberty, it decreases in size, and is very small in older adults. We don’t know why the thymus gland atrophies at such a fast rate but preventing it can be helpful in prolonging health.
What is Thymulin?
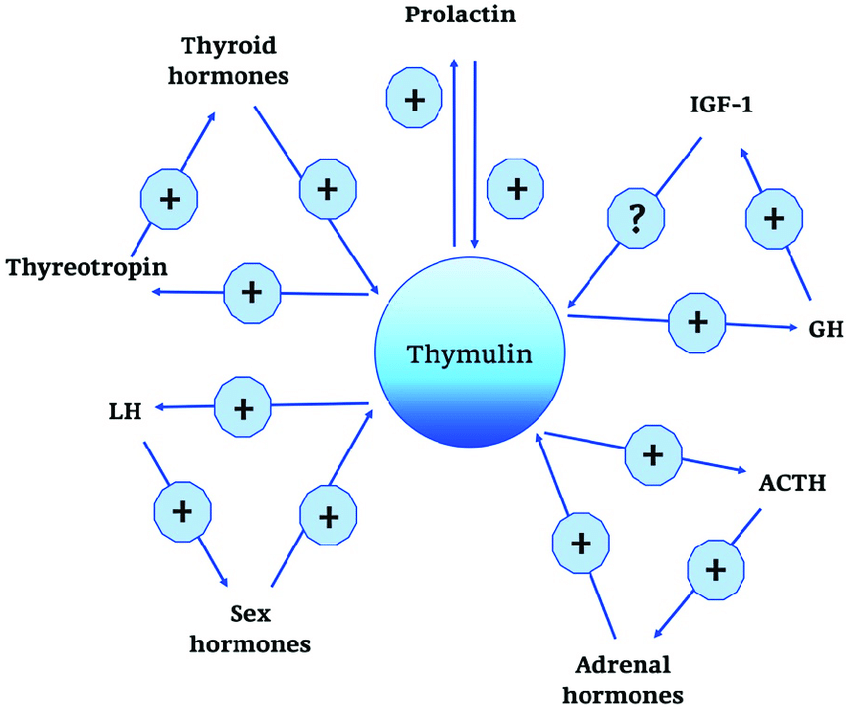
The thymus produces and secretes the hormone thymosin, as well as thymopoietin and thymulin. Thymulin is involved in the creation of cells responsible for driving your body’s immune response. It is a nonapeptide hormone consisting of nine amino acids and is primarily produced by thymic epithelial cells. Thymulin is sometimes used interchangeably with Thymalin.
It’s also known as a neuroendocrine hormone because of its role in the immune system, exerting immunoregulatory actions that contribute to overall health and vitality. As we age, the levels of Thymulin decline leading to potential imbalances in the immune system with associated health issues.
7 Benefits of Thymulin
1. Immune System Support:
Thymulin's primary function is to regulate immune responses. By modulating the activity of T cells and other immune components, Thymulin contributes to a finely tuned defense against pathogens.
2. Anti-Aging Properties:
Research suggests that Thymulin may play a role in slowing down the aging process. Its involvement in immune regulation is intricately linked to overall health and longevity.
3. Stress Response:
Thymulin has also been implicated in the body's response to stress. Its neuroendocrine nature allows it to influence stress pathways, potentially mitigating the impact of stressors on the body.
4. Wound Healing and Tissue Repair:
Some studies indicate that Thymulin may play a role in wound healing and tissue repair. This could be attributed to its influence on immune cells and their functions.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
Thymulin has been associated with anti-inflammatory actions, which could be beneficial in conditions where excessive inflammation is a contributing factor.
6. Metabolic Regulation:
There is some evidence suggesting that Thymulin may have an impact on metabolic processes. Its role in neuroendocrine signaling may influence metabolic pathways, potentially contributing to overall metabolic health.
7. Cognitive Function:
While research is in the early stages, there are indications that Thymulin may have implications for cognitive function. Its role in neuroendocrine regulation may extend to the central nervous system.
Zinc + Thymulin
Zinc and thymulin are relevant for normal immune functions. The activity of thymulin is dependent on the presence of zinc. Studies have shown that serum thymulin activity was decreased as a result of zinc deficiency but was corrected with zinc supplementation.
Scientific studies have delved into the multifaceted roles of Thymulin, revealing its potential as a key player in immune function and anti-aging processes. Researchers have explored its interactions with various components of the immune system, shedding light on how Thymulin may be harnessed for therapeutic purposes.
Research
Scientific studies have delved into the multifaceted roles of Thymulin, revealing its potential as a key player in immune function and anti-aging processes. Researchers have explored its interactions with various components of the immune system, shedding light on how Thymulin may be harnessed for therapeutic purposes.
da Silva AL, Martini SV, Abreu SC, Samary Cdos S, Diaz BL, Fernezlian S, de Sá VK, Capelozzi VL, Boylan NJ, Goya RG, Suk JS, Rocco PR, Hanes J, Morales MM. DNA nanoparticle-mediated thymulin gene therapy prevents airway remodeling in experimental allergic asthma. J Control Release. 2014 Apr 28;180:125-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.02.010. Epub 2014 Feb 17. PMID: 24556417; PMCID: PMC3992277.
Khavinson, V. Kh., B. I. Kuznik, and G. A. Ryzhak. “Peptide Bioregulators: A New Class of Geroprotectors. Message 1: Results of Experimental Studies.” Advances in Gerontology 3, no. 3 (July 2013):225–35. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079057013030065
J. Haddad, N. E. Saade, B. Safieh-Garabedian. Thymulin: An Emerging Anti-Inflammatory Molecule. Current Medicinal Chemistry - Anti-Inflammatory & Anti-Allergy Agents 4(3):333-338. June 2005 DOI:10.2174/1568014054065195
Reggiani PC, Morel GR, Cónsole GM, Barbeito CG, Rodriguez SS, Brown OA, Bellini MJ, Pléau JM, Dardenne M, Goya RG. The thymus-neuroendocrine axis: physiology, molecular biology, and therapeutic potential of the thymic peptide thymulin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Feb;1153:98-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03964.x. PMID: 19236333; PMCID: PMC2688715.
Reggiani PC, Schwerdt JI, Console GM, Roggero EA, Dardenne M, Goya RG. Physiology and therapeutic potential of the thymic peptide thymulin. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(29):4690-6. doi: 10.2174/1381612820666140130211157. PMID: 24588820.
Goya RG, Brown OA, Pléau JM, Dardenne M. Thymulin and the neuroendocrine system. Peptides. 2004 Jan;25(1):139-42. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2003.11.002. PMID: 15003367.
Nasseri B, Zaringhalam J, Daniali S, Manaheji H, Abbasnejad Z, Nazemian V. Thymulin treatment attenuates inflammatory pain by modulating spinal cellular and molecular signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 May;70:225-234. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.02.042. Epub 2019 Mar 6. PMID: 30851702.
Reggiani PC, Poch B, Cónsole GM, Rimoldi OJ, Schwerdt JI, Tüngler V, Garcia-Bravo MM, Dardenne M, Goya RG. Thymulin-based gene therapy and pituitary function in animal models of aging. Neuroimmunomodulation, 18(5):350-356, 22 Sep 2011
Lunin SM, Novoselova EG.Thymus hormones as prospective anti-inflammatory agents. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 14(8):775-786, 01 Aug 2010
Lunin SM, Khrenov MO, Novoselova TV, Parfenyuk SB, Novoselova EG. Thymulin, a thymic peptide, prevents the overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and heat shock protein Hsp70 in inflammation-bearing mice. Immunol Invest, 37(8):858-870, 01 Jan 2008
Saadé NE, Atweh SF, Jabbur SJ, Dardenne M, Bach JF, Safieth-Garabedian B. A thymulin analogue peptide with powerful inhibitory effects on pain of neurogenic origin. Neuroscience, 119(1):155-165, 01 Jan 2003